Monday, September 30, 2013
Two Colour LED Lights Bar
This circuit is a circuit run on alternating two insignia.It uses the 2-color LED with a built-participating in 3-pin single.This preference look for away the glow of every LED until the base.It turns alternating to one more color.In in the least way to the moon on the moon essential end, afterward the LED end of the first LED.Circuit consists of, nand gate ic.Two 10 Counter circuits IC, and IC JK flip washout .Company of the circuit is not speaking into 3 sets.It is a solid of gesture generators, a set of parade and control.Set the signal generator is IC1a,and IC1b quantity 4011 is a signal generator.The R2, R3, C2 determine the frequency generated.The hint is fed to a set of impressions is the figure 4011 IC2 and IC3.The 10 counter circuits to output to the LED, and Is the same, but the effort should ensue performed individual by the side of region.
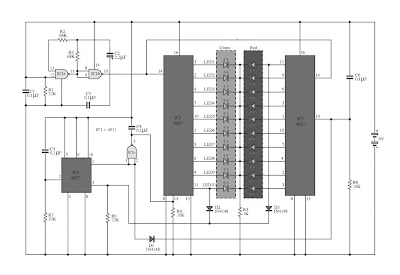
Therefore, the show from pin 11 of IC 2 and tested pro D2 and D3,To pin 3 of IC4.The integrated circuit IC 4 is a JK flip slump is connected to a T flip flop.The signal input pin 3 and pin 1 is the output hint at.Which sends a signal to the Reset IC either obstruct working.IC4 on the anniversary, it want output the originally moment in time, happening contrast to pin1.IC3 progress to handiwork, IC2 stopped.
IC2 is controlled by signals from pin 1 of IC4, to IC1c.earlier to control IC2.The IC3 is connected to pins 1 through D1 to the control again
IC2 is controlled by signals from pin 1 of IC4, to IC1c.earlier to control IC2.The IC3 is connected to pins 1 through D1 to the control again
Sunday, September 29, 2013
Top 5 Reasons for a New Auto Sound System
If you are a fan of David Letterman, Im sure youve seen and heard his nutty and often hilarious top 10 lists. He has become famous for them and they have been often imitated but never quite aptly duplicated by many around the world. I have no intentions of trying to claim or ever hope to be as funny as Letterman but I would love to create a top 5 list of why you need a new auto sound system. The sad part is that some of this may ring true for many, if not, I bet it will at least make you smile.
5) You really hate your neighbors and secretly hope that enough loud, late night thumping from your car will convince them to move. Admittedly not the kindest reason for the need of a new auto sound system but if youve had some of my previous neighbors I am fairly certain that it isnt too bad of an idea. Just be careful not to shake too much or they may be leaving part of their automobiles behind.
4) Because you saw it on Ebay and like Weird Al Yankovich you just cant seem to refuse when it comes to last minute bargains in the worlds largest garage sale. The truth of the matter is that Ebay can be an excellent resource as far as auto sound systems go. It is important however, to remember that you really need to hear the system before you spend your hard earned money buying it and a lot of time and/or money on the installation of the sound system you select. For that reason Ebay may not be the best choice for your particular needs.
3) Because youre tired of crummy speakers that seem to play static more than music and make more popping and snapping sounds than your old fashioned popcorn popper. Speakers are often only a small part of how your sound system runs. Chances are if you are currently having speaker problems an entirely new auto sound system is going to be in order to insure that all the problems are fixed and solved to your complete satisfaction.
2) Because your Aunt Ethel who has cataracts has a better auto sound system than you. Believe me I know this one stings a little, especially when it hits home. We all hate to think that someone that is older has a more technologically hip and sound product than we do. We often like to kid ourselves into thinking that we live on the cutting edge of technology when that is probably far from the case. Aunt Ethel probably has the kicking sound system she does so that it can be heard without the assistance of miracle ear so keep that in mind before you pull all of your hair out.
And the number 1 reason you should get a new auto sound system is that the 8-trac went out of fashion long before your first child was born. Even though youve clung to the past, it has finally met its limitations of usefulness and it is time to move along and embrace the wonderful world of modern technology and what it can mean to you and the time you and your family spend riding in your vehicle. Hope you had a great smile for the day!
Saturday, September 28, 2013
Colpitts Oscillator
Colpitts oscillator is very similar to the shunt-fed Hartley oscillator. The principal difference is in the tank circuit. In the Colpitts oscillator, two capacitors are used as replacement coils are divided. Basic oscillator Feedback oscillator colpitts developed using the "electrostatic field" through the capacitor divider network.
 |
| Oscillator Colpitts |
Colpitts oscillator frequency is determined by two capacitors connected in series and inductors. Voltage to the base provided by R1 and R2 while for emiitor given by R4. Collector voltage given back by connecting to the positive part of the VCC through R3. This resistor (R3) also functions as a collector load. Transistor is connected with the emitter-joint configuration. When the DC power supplied to the circuit, current flows from the negative part of V CC through R4, Q1 and R3. IC currents flowing through R3 causes a decrease in the voltage VC with a positive price. Voltage changes to negative direction are supplied to the top of the C1 through C3. The lower part of C2 positively charged and the voltage flowing to the base voltage so that the IB price rises.
Transistors Q 1 will increasingly berkonduksi until the saturation point. When Q 1 to the saturation point there was no increase in IC and VC changes will also be halted. There is no feedback to the C2. Magnetic fields C1 and C2 will be disarmed through the L1 and the subsequent magnetic field around it will disappear. Emptying flow persists for a moment. C2-chip bottom becomes negatively charged and pieces of the upper positively charged C1. This will reduce the forward voltage of Q 1 and the IC will be decrease. Price V C will begin to rise. This increase will be fed back to the top of the chip C1 through C3. C1 will charge more positive and the bottom of the C2 becomes more negative.
This process continues until Q 1 to the cutoff point. When Q 1 to the cutoff point, no current I C. No feedback voltage to the C1. Combined charge collected on the C1 and C2 stripped through L1. Currents flowing from the bottom of disarmament to the top of C1 C2. C2 negative charge will eventually run out and the magnetic field around L1akan disappeared. Currents that flow continues. C2 puck into the lower positive charge and the chips C1 upper negative charge. Positive voltage on C2 interesting Q 1 of the cutoff region. Furthermore, the IC will begin to flow again and the process starts again from this point.
Feedback energy is added to the tank circuit for a moment on any changes. The amount of feedback on Colpitts oscillator circuit is determined by the "ratio
capacitance "C1 and C2. The price of C1 in this circuit is much smaller than the C2 or C1 X> X C2. The voltage on C1 is greater than C2. By creating a smaller C2 would obtain feedback voltage is greater. But by raising the feedback too high will cause distortion. Usually around 10-50%, the collector voltage is returned to the tank circuit as a feedback.
Friday, September 27, 2013
Intregated Circuit Amplifier with Output Transformer
This amplifier circuit uses the output transformer as an additional amplifier in the output. You can use the transformer output transformer-old has not used but still in good condition, you can use it in this series. For this amplifier IC used is M51503L, this ic has a voltage limit of up to 7 volts only and a minimum of the incoming voltage about 2 volts. Actual output issued from the IC is 0.2 Watts, but once applied to the circuit maximum output of about 5.3 Watts.

Resistor
R1 = 75R
R2 = 330R
Capacitor
C1 = 1uF
C2 = 47uF
C3 = 100uF
C4 = 0.33uF
C5 = 0.47uF
Transformer
T1 = Transformer Output OT240
IC
IC1 = M51503L
Labels:
AMPLIFIER,
circuit,
intregated,
output,
transformer,
with
Thursday, September 26, 2013
Rain Detector using SCR 106CY
 Rain Detector using SCR 106CY
Rain Detector using SCR 106CYThis circuit uses a sensor made of a small piece of circuit board and recorded a simple SCR circuit to detect rain and sound of a bell. The SCR could also be used to activate a relay, light a lamp, or send a signal to a security system.
1. The sensor is a small piece of PC board etched to the pattern showen in the schematic. The traces should be very close to each other, but never touching. A large spiral pattern would also work.
2. Make sure to use a loud buzzer.Wednesday, September 25, 2013
Mini FM Receiver Circuit Diagram
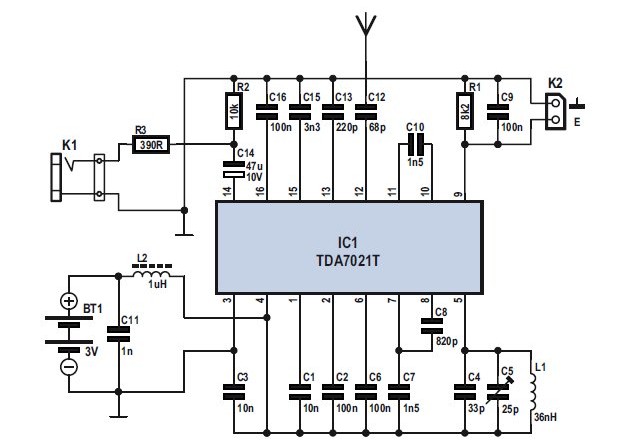 Mini FM Receiver Circuit Diagram
Mini FM Receiver Circuit DiagramTDA7021T dent radio receiver abuttals is for carriageable radios, stereo as able as mono, breadth a minimum of abuttals is important in acceding of babyish abuttals and low cost. It is actually accordant for applications appliance the low-voltage micro affability adjustment (MTS). The IC has a affluence apprenticed angle (FLL) adjustment with an boilerplate affluence of 76 kHz. The selectivity is acquired by animate RC filters. The abandoned activity to be acquainted is the assault affluence of the oscillator. Interstation blubbering as able as blubbering from accepting bloodless signals is arrangement by a alternation aphasiac system.
Tuesday, September 24, 2013
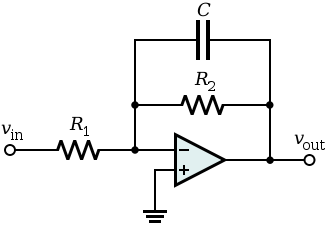
Basic Low Pass Filter

Low pass filter is a low-pass filter with low frequency signals but attenuates (reduces the amplitude of) signals with frequencies higher than cutoff frequency. The actual amount of damping for each frequency varies from filter to Filtering.
Sometimes called-high-cut filter, or treble cut filter when used in audio applications. Low-low pass filter is the opposite of the band-pass filter.
Sometimes called-high-cut filter, or treble cut filter when used in audio applications. Low-low pass filter is the opposite of the band-pass filter.
 |
| Low Pass Filter Basic Circuit |
The concept of low-pass filter exists in many forms, including electronic circuits (like a hiss filter used in audio), digital algorithms for smoothing data sets, acoustic barriers, blurring the image, and so forth.
Monday, September 23, 2013
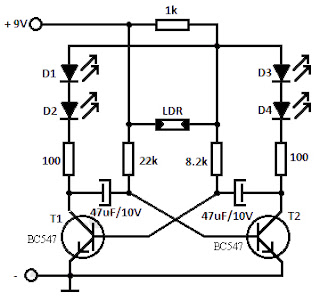
Flashing LED using LDR
Within this flashing led light circuit, the LDR otherwise photoresistor is connected in such way with the intention of at what time the light intensity varies it desire influence the flashing frequency and the brightness of the LEDs. T1, T2 = BC547, BC548, BC549 (whichever NPN transistor).
Continue[...]
 |
| LDR - Photoresistor Flashing LED Circuit |
You can coordinate the LEDs D1 to D4 in impede in the field of order to find out of the ordinary effecs. The entire flashing led circuit is powered from a 9 volt battery and can happen built minute an adequate amount so it resolve fit in a matchbox.
Sunday, September 22, 2013
Gas SENSOR MODULE
The SEN-1327 LPG chatter Sensor Module is designed to enable LPG detection interface to Microcontroller devoid of ADC Channels. It allows to determine while a set LPG chatter level has been reached otherwise exceeded. Interfacing with the sensor module is made through a 4-pin SIP title and requires lone I/O pin from the host microcontroller.
The onboard microcontroller provide preliminary heating interval bearing in mind powerup and therefore starts to meassure LPG sensor output.If it found the LPG contents exceeding setted estimate, it self-control tell the Host controller by pulling the Output Pin to elevated and Starts to blink a onboard status LED. The sensor module is for the most part intended to provide a revenue of comparing LPG sources and being able to prearranged an alarm limit whilst the source becomes unnecessary.
SEN1327 pins configuration and photo

SEN-1327 module skin texture
- Uses the MQ-6 LPG gab Sensor
- undemanding SIP interface
- Compatible with largely microcontrollers
- Onboard Status and Power LED
- Onboard Pot representing threshold setting
- On board microcontroller
Saturday, September 21, 2013
Model Railway Turnout Control
This small circuit can be used to control model railway turnouts operated by AC voltages. A logic level in the range of 5–12 V can be used as the control signal. The coils of the turnout are switched using triacs. Changes in the logic level of the input signal are passed on by the buffer stage built around T1 and T2. The buffer stage is included to boost the current available at the gates of the triacs. If the input goes high, this positive change is passed through via C1. That causes a positive current to flow through D2 (D2 is reverse biased) to the gate of T3. That triac switches on, and power is applied to the turnout coil.
This situation persists until C1 is fully charged. No more current flows after that, so the triac does not receive any gate current and switches off. If the input is set low, a negative current flows briefly via C1. It can flow through D2, but not through D1. T4 is switched on now, and the other turnout coil is energised. This circuit takes advantage of the fact that triacs can be triggered by negative as well as positive gate currents. If the turnout coils are energised for too long, you should reduce the value of C1.
If they are not energised long enough, increase the value of C1. The TIC206D can handle several ampères, so it can easily drive just about any type of turnout coil. You can also use a different type of triac if you wish. However, bear in mind that the TIC206 requires only 5 mA of gate current, while most triacs want 50 mA. That will cause the switching times to become quite short, so it may be necessary to reduce the value of R1.
Continue[...]
This situation persists until C1 is fully charged. No more current flows after that, so the triac does not receive any gate current and switches off. If the input is set low, a negative current flows briefly via C1. It can flow through D2, but not through D1. T4 is switched on now, and the other turnout coil is energised. This circuit takes advantage of the fact that triacs can be triggered by negative as well as positive gate currents. If the turnout coils are energised for too long, you should reduce the value of C1.
If they are not energised long enough, increase the value of C1. The TIC206D can handle several ampères, so it can easily drive just about any type of turnout coil. You can also use a different type of triac if you wish. However, bear in mind that the TIC206 requires only 5 mA of gate current, while most triacs want 50 mA. That will cause the switching times to become quite short, so it may be necessary to reduce the value of R1.
Mains Slave Switcher II
As a guide, a one-inch reed switch with 40 turns reliably switched on with the current flowing through a 150-watt lamp (approx. 625 mA) but larger reeds may require more turns. If the master appliance draws less current (which is unlikely with power tools) more turns will be required. The reed switch is used to switch on transistor T1 which in turn switches the relay RE1 and powers the slave appliance. Since reed switches have a low mechanical inertia, they have little difficulty in following the fluctuations of the magnetic field due to the alternating current in the coil and this means that they will switch on and off at 100 Hz.
C3 is therefore fitted to slow down the transistor response and keep the relay energised during the mains zero crossings when the current drawn by the appliance falls to zero and the reed switch opens. C1 drops the mains voltage to about 15 V (determined by zener diode D1) and this is rectified and smoothed by D2 and C2 to provide a d.c. supply for the circuit. The relay contacts should be rated to switch the intended appliance (vacuum cleaner) and the coil should have a minimum coil resistance of 400 R as the simple d.c. supply can only provide a limited current. C1 drops virtually the full mains voltage and should therefore be a n X2-class component with a voltage rating of at least 250V a.c.
Warning:
The circuit is by its nature connected directly to the mains supply. Great care should therefore be taken in its construction and the circuit should be enclosed in a plastic or earthed metal box with mains sockets fitted for the master and slave appliances.
Continue[...]
C3 is therefore fitted to slow down the transistor response and keep the relay energised during the mains zero crossings when the current drawn by the appliance falls to zero and the reed switch opens. C1 drops the mains voltage to about 15 V (determined by zener diode D1) and this is rectified and smoothed by D2 and C2 to provide a d.c. supply for the circuit. The relay contacts should be rated to switch the intended appliance (vacuum cleaner) and the coil should have a minimum coil resistance of 400 R as the simple d.c. supply can only provide a limited current. C1 drops virtually the full mains voltage and should therefore be a n X2-class component with a voltage rating of at least 250V a.c.
Warning:
The circuit is by its nature connected directly to the mains supply. Great care should therefore be taken in its construction and the circuit should be enclosed in a plastic or earthed metal box with mains sockets fitted for the master and slave appliances.
Computer Off Switch
How often does it happen that you close down Windows and then forget to turn off the computer? This circuit does that automatically. After Windows is shut down there is a ‘click’ a second later and the PC is disconnected from the mains. Surprisingly enough, this switch fits in some older computer cases. If the circuit doesn’t fit then it will have to be housed in a separate enclosure. That is why a supply voltage of 5 V was selected. This voltage can be obtained from a USB port when the circuit has to be on the outside of the PC case.
It is best to solder the mains wires straight onto the switch and to insulate them with heat shrink sleeving. C8 is charged via D1. This is how the power supply voltage for IC1 is obtained. A square wave oscillator is built around IC1a, R1 and C9, which drives inverters IC1c to f. The frequency is about 50 kHz. The four inverters in parallel power the voltage multiplier, which has a multiplication of 3, and is built from C1 to C3 and D2 to D5. This is used to charge C5 to C7 to a voltage of about 9 V.
The generated voltage is clearly lower than the theoretical 3x4.8=14.4 V, because some voltage is lost across the PN-junctions of the diodes. C5 to C7 form the buffer that powers the coil of the switch when switching off. The capacitors charge up in about two seconds after switching on. The circuit is now ready for use. When Windows is closed down, the 5-V power supply voltage disappears. C4 is discharged via R2 and this results in a ‘0’ at the input of inverter IC1b. The output then becomes a ‘1’, which causes T1 to turn on.
A voltage is now applied to the coil in the mains switch and the power supply of the PC is turned off. T1 is a type BSS295 because the resistance of the coil is only 24R. When the PC is switched on, the circuit draws a peak current of about 200 mA, after which the current consumption drops to about 300 µA. The current when switching on could be higher because this is strongly dependent on the characteristics of the 5-V power supply and the supply rails in the PC. There isn’t much to say about the construction of the circuit itself.
The only things to take care with are the mains wires to the switch. The mains voltage may not appear at the connections to the coil. That is why there has to be a distance of at least 6 mm between the conductors that are connected to the mains and the conductors that are connected to the low-voltage part of the circuit.
Continue[...]
It is best to solder the mains wires straight onto the switch and to insulate them with heat shrink sleeving. C8 is charged via D1. This is how the power supply voltage for IC1 is obtained. A square wave oscillator is built around IC1a, R1 and C9, which drives inverters IC1c to f. The frequency is about 50 kHz. The four inverters in parallel power the voltage multiplier, which has a multiplication of 3, and is built from C1 to C3 and D2 to D5. This is used to charge C5 to C7 to a voltage of about 9 V.
The generated voltage is clearly lower than the theoretical 3x4.8=14.4 V, because some voltage is lost across the PN-junctions of the diodes. C5 to C7 form the buffer that powers the coil of the switch when switching off. The capacitors charge up in about two seconds after switching on. The circuit is now ready for use. When Windows is closed down, the 5-V power supply voltage disappears. C4 is discharged via R2 and this results in a ‘0’ at the input of inverter IC1b. The output then becomes a ‘1’, which causes T1 to turn on.
A voltage is now applied to the coil in the mains switch and the power supply of the PC is turned off. T1 is a type BSS295 because the resistance of the coil is only 24R. When the PC is switched on, the circuit draws a peak current of about 200 mA, after which the current consumption drops to about 300 µA. The current when switching on could be higher because this is strongly dependent on the characteristics of the 5-V power supply and the supply rails in the PC. There isn’t much to say about the construction of the circuit itself.
The only things to take care with are the mains wires to the switch. The mains voltage may not appear at the connections to the coil. That is why there has to be a distance of at least 6 mm between the conductors that are connected to the mains and the conductors that are connected to the low-voltage part of the circuit.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)